From EHRs to AI Tools: 16 Essential Healthcare Software Solutions in 2025-26
Author

Subject Matter Expert


Date
Book a call
Key Takeaways
- The U.S. healthcare software market is picking up speed in 2025. AI adoption, tighter compliance rules, and the demand for scalable digital platforms are driving this growth. Providers are investing faster than ever, looking for ways to cut costs while improving patient outcomes.
- Fifteen software solutions are crucial to the future of care. They consist of HIPAA-compliant EHRs, telemedicine applications, AI analytics, and remote patient monitoring devices.
- Healthcare software should be developed on three pillars: compliance, data security, and scalability. These characteristics form the basis of digital trust and the path to successful adoption.
- Patient care is being transformed by AI-driven healthcare apps. They predict risks before they escalate. They personalize treatments based on individual needs. These changes combined are becoming the future of digital health.
The Push for Interoperability and AI in Healthcare Software

Kunal Kumar
COO , GeekyAnts
The shift highlights how regulatory pressure aligns with patient expectations. Providers that design platforms around fluid data exchange and predictive intelligence will not only stay compliant but also earn trust by delivering care that feels connected and proactive.
Benefits of Healthcare Software Solutions
Healthcare software has turned out to be the key that can make hospitals, clinics, and practices potentially safe, sustainable, and financially viable in providing healthcare. In 2025, the benefits are directly correlated with the ways under which providers are paid, how patients receive care, and how the systems continue to operate in a rapidly evolving regulatory environment.
- Reduced Admin Burden & Burnout
The paperwork load, especially for physicians and nurses, is also being reduced with the aid of automated scheduling, billing, and clinical documentation, which allows them to dedicate more time to patients. This change will solve one of the most urgent dangers of U.S. healthcare: staff burnout.
- Regulatory & Compliance Assurance
Every healthcare provider must follow HIPAA, FHIR, CMS rules, and the constantly evolving ONC requirements. Platforms built with compliance at their core make this easier, reducing the risk of penalties and protecting patient data from breaches.
- Quality & Safety Improvements
Clinical decision support systems and predictive functions identify potential hazards at a better time than manual surveillance would have ever noticed. Patients and regulators can measure the direct impacts listed in the previous section because hospitals with these solutions report decreased medication errors, reduced readmission rates, and safe surgical outcomes.
- Access & Equity
Telehealth systems, distance healthcare, and remote patient technology are opening the doors to the rural population and underserved populations. These systems are ensuring care in places it was never before, sealing disparities that have always characterized U.S. healthcare.
- Scalability & Real-Time Data
Cloud computing enables health systems to expand without the restrictions inherent in old IT. From a single clinic to a national network, providers can scale while still accessing real-time patient data across locations. Such agility is essential within an environment where the demand and compliance requirements change on an ongoing basis.
16 Essential Healthcare Software Solutions in the U.S.
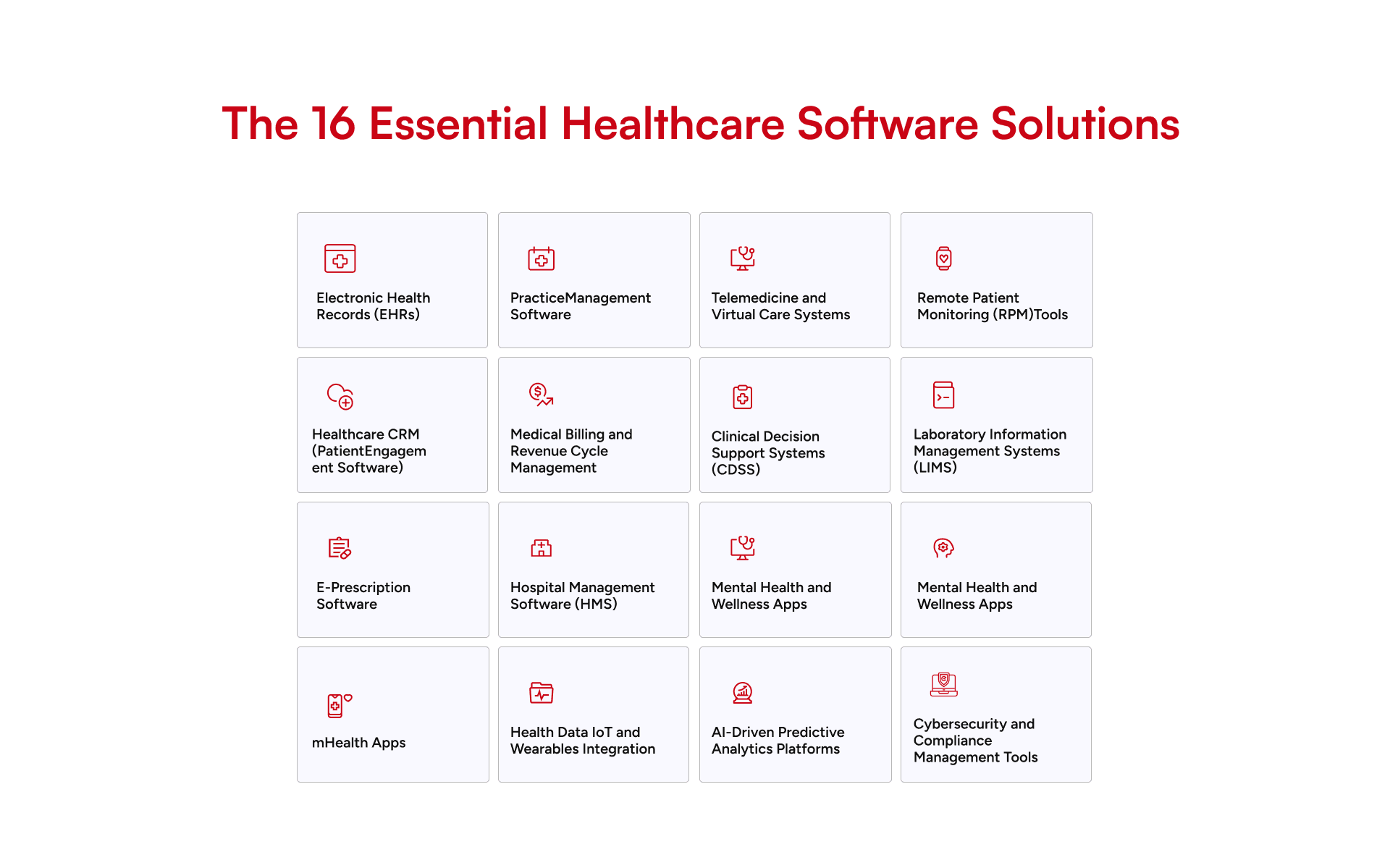
1. Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
2. Practice Management Software
3. Telemedicine and Virtual Care Systems.
4. Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) Tools
5. Healthcare CRM (Patient Engagement Software)
6. Medical Billing and Revenue Cycle Management
7. Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS)
8. Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS)
9. Radiology and Imaging Software (PACS, RIS).
10. E-Prescription Software
11. Hospital Management Software (HMS)
12. Mental Health and Wellness Apps
13. mHealth Apps
14. Health Data IoT and Wearables Integration
15. AI-Driven Predictive Analytics Platforms
16. Cybersecurity and Compliance Management Tools
The Problem of Healthcare Software Development: Implementation Problems and How to Overcome Them
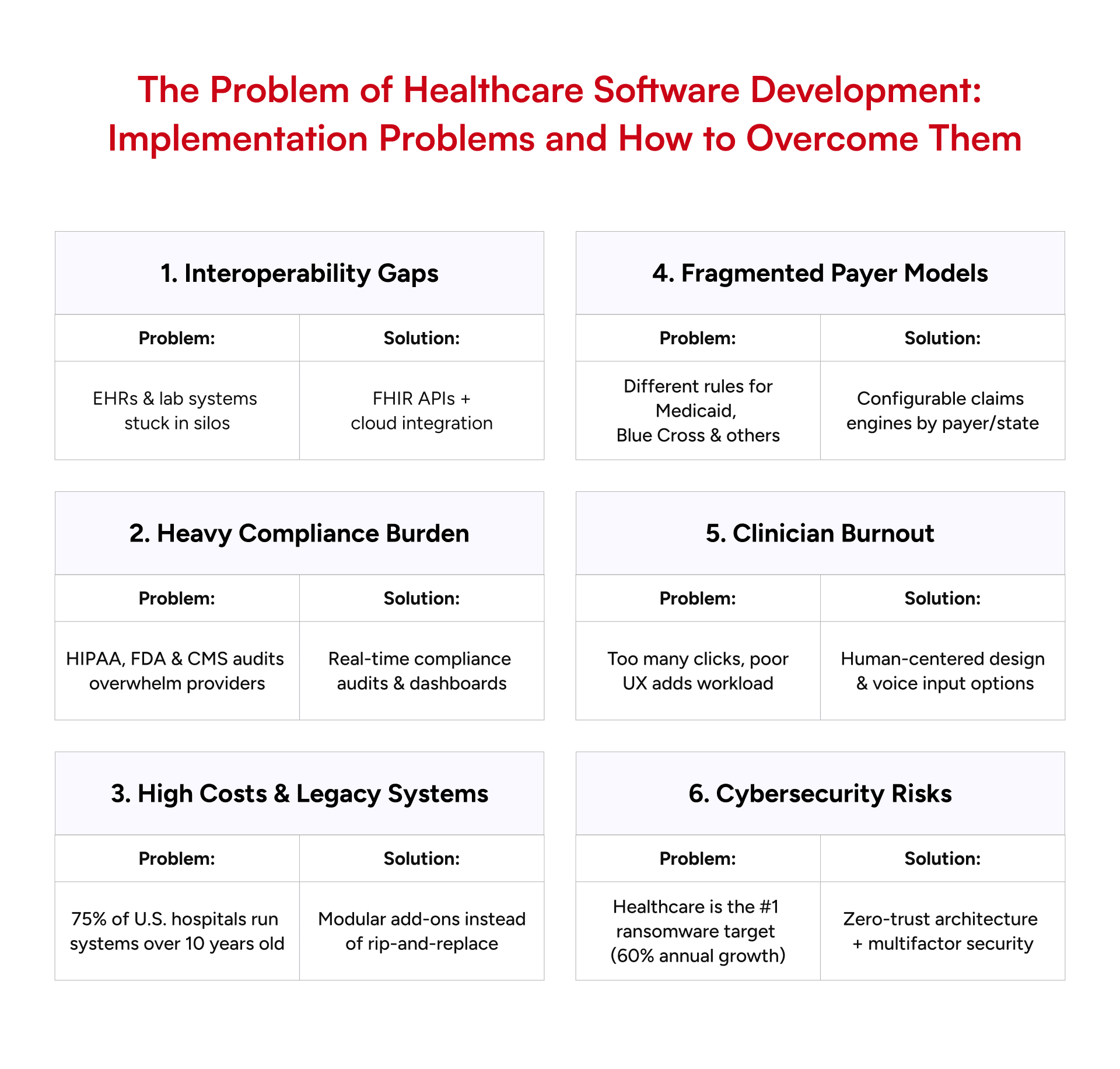
Healthcare software development in the United States is a trade-off between clinical reality, regulatory complexity, and financial constraint. These are not abstract problems but manifest themselves through project overruns, fines, and patient wait times.
- Interoperability Gaps: A large portion of EHRs and lab systems remain in silos. Lack of compatibility in data exchange is a major hindrance to patient records, and practitioners are compelled to deal with partially available information. The way out of this is to adopt FHIR-based APIs and cloud-based integration layers, which are capable of creating real-time data bridges between the old architectures and the new applications.
- Regulatory Agencies: Providers are exposed to a heavy compliance burden due to HIPAA, FDA software controls, and CMS reporting requirements. In this regard, as with having to conduct compliance audits constantly, the sensible way to resolve this is to build compliance into the software, in the form of real-time compliance audits and dashboard summaries that show the true state of encryption and consent.
- High Costs and Lagging Integration: More than three-quarters of hospitals in the U.S. have core systems that are more than 10 years old. Integrating modern AI or telehealth tools into such environments inflates costs and risks downtime. Vendors succeed by using modular add-ons that wrap around legacy systems instead of “rip-and-replace.”
- Fragmented Payer Models: Unlike Europe’s centralized systems, U.S. payers each have their own rules for prior authorizations and reimbursements. A single workflow that works for Medicaid may fail for Blue Cross. The solution: configurable claims engines that adapt rules by payer and state, reducing manual work.
- Clinician Adoption & Burnout: Software often adds clicks instead of removing them. Clinicians resist tools that slow them down, even if compliance improves. Teams that succeed use human-centered design—involving physicians early in UX testing, creating voice-input options, and aligning with real workflows.
- Cybersecurity Stress: As in 2025, healthcare became the leading ransomware franchise with attacks growing at an annual rate of 60 percent. In addition to HIPAA, payers are currently requiring proof of endpoint detection, multifactor authentication, and encrypted backups. The best bet is zero-trust architectures, which assume that all access requests may be unfriendly.
How Costly Is Healthcare Software Development in the U.S.?
The cost of software development in healthcare is widely spread across the spectrum of scope measures, diligence, and regulatory requirements. The requirements for HIPAA compliance, data security, and interoperability increase the cost of development and maintenance in the U.S.
Estimated Cost of Healthcare Software Development (U.S. Region)
| Project Scope | Estimated Cost Range (USD | Timeline (Months) |
|---|---|---|
|
MVP / Pilot Solution (basic EHR, telemedicine app, or patient portal)
| $120,000 – $250,000 | 4 – 6 |
Mid-Scale Platform (integrated practice management + billing + compliance)
| $250,000 – $600,000 | 6 – 12 |
|
Enterprise-Grade System (full hospital management system, AI tools, IoMT integration)
| $600,000 – $1.5M+ | 12 – 18 |
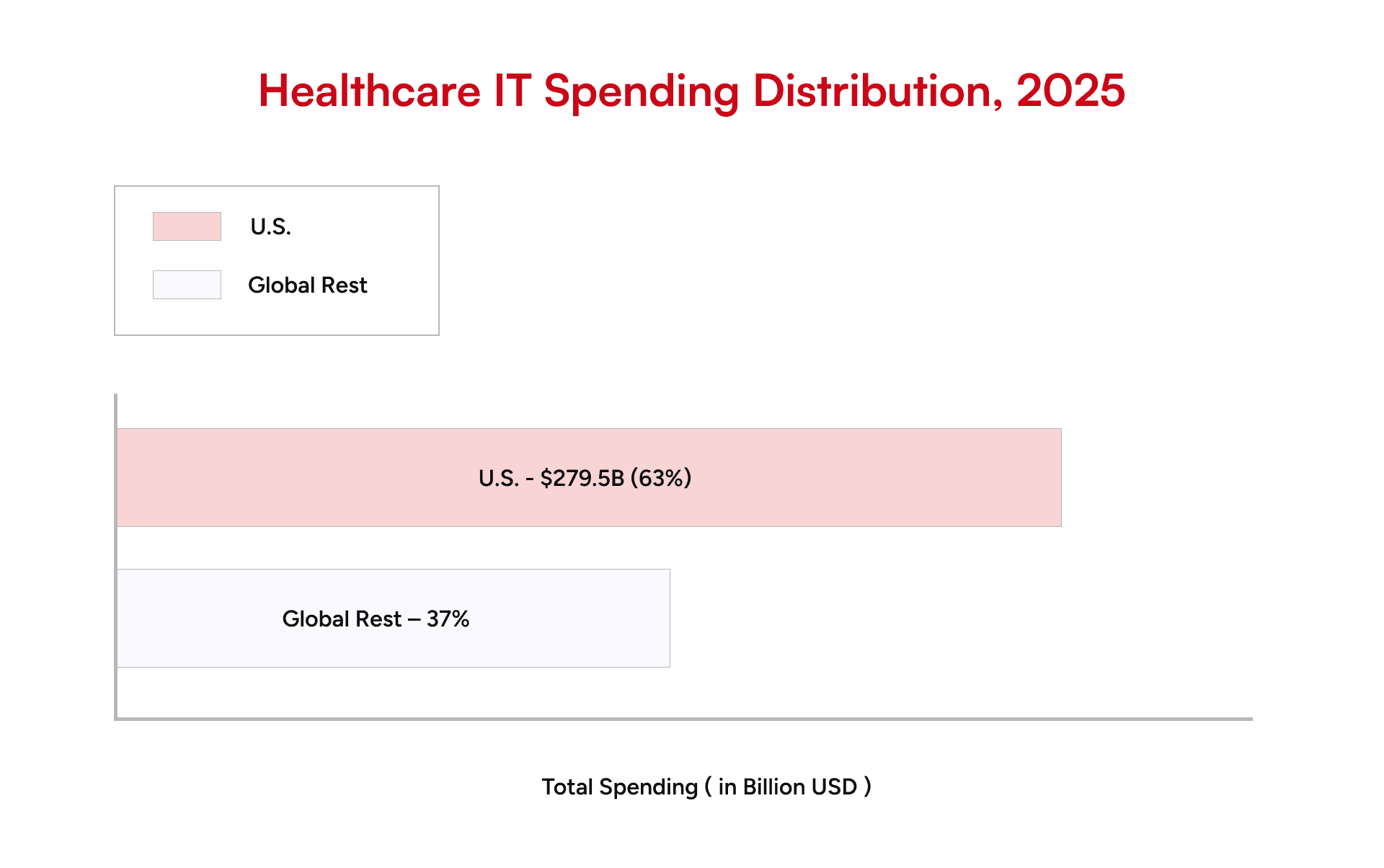
These numbers reflect U.S. labor and compliance costs. Outsourcing part of the build to offshore engineering teams, while keeping sensitive modules U.S.-based, can reduce costs by 25-35%.
Key Factors Driving Healthcare Software Development Costs
The cost of building healthcare software in the U.S. sits at the intersection of technical ambition and strict regulation. CIOs and CFOs are expected to deliver platforms that scale while demonstrating compliance from day one. Several factors shape both the timeline and the budget.
1. Scope of Features
2. Compliance and Security
3. Integration Complexity
4. Technology Stack Choices
5. Customization vs. Off-the-Shelf
6. Workforce Costs
7. Ongoing Maintenance
Which Businesses Should Invest in Healthcare Software?
Not every business needs a full-scale hospital management system. The decision comes down to size, specialization, and long-term goals.
- Small Clinics and Private Practices
- Mid-Sized Providers
- Large Hospitals and Health Systems
- Specialty Centers
- Payers and Insurers
- Pharma and Research Organizations.
- Remote Care Providers and Home Health.
The Future of Healthcare Software: 2025 and Beyond
How GeekyAnts Helps Providers Turn Challenges Into Digital Solutions
Among healthcare software developers, GeekyAnts stands out for developing systems that align with the strict requirements of the U.S. market yet remain practical worldwide. With HIPAA compliance, security, and scalability built in, our products help providers embrace product innovation without sacrificing reliability or trust.
- Type 1 Diabetes Management App – A mobile and web platform that lets families track glucose, sleep, and insulin intake in real time. The system transformed daily disease management into a connected, supportive experience for both patients and caregivers.
- IoT Health Platforms for Athletes and Amputees – Connected devices that monitored hydration and performance, reducing the risk of injury while helping users push their limits safely.
- Marigold Health Mental Wellness App – A digital therapy solution where patients could join group therapy sessions over text, offering a discreet, accessible way to seek mental health support—an area often underserved by traditional systems.





