Table of Contents
Building Intelligent Chatbots: Enhancing User Experience with Natural Language Processing
Author
Date

Book a call
Let's talk about building smart chatbots and how they make our lives easier by understanding and responding to natural language. Chatbots have become increasingly important in today's world, being utilized in various industries like e-commerce, customer support, and healthcare. But before we get into the details, let's first understand some key terms: artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and what exactly chatbots are.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) is a computer system that helps perform tasks that require human intelligence.
- Machine learning is a subset of AI that focuses on recognizing patterns using algorithms.
- Supervised machine learning involves using data that already has predefined annotations and labels, while unsupervised learning seeks to find patterns in datasets without any predefined labels.
- Natural language processing (NLP) is a part of machine learning that allows us to interact with computers using everyday language.
- Chatbots are software programs that enable conversations between users and systems, can receive user queries, understand the text, and provide relevant responses based on context.
Since their inception in the 1960s, chatbots have come a long way.
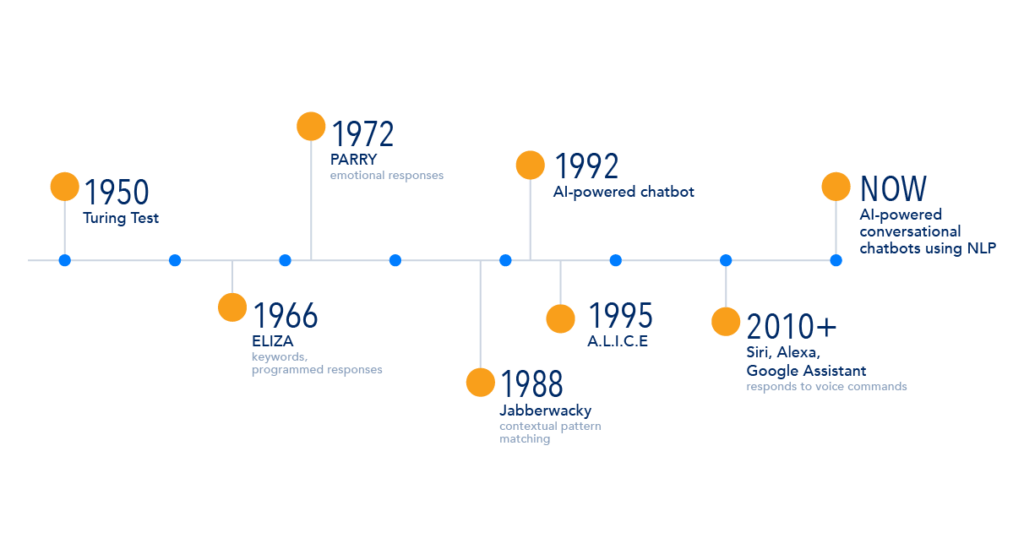
Eliza, the first chatbot, simulated a psychotherapist. In the 2000s, A.L.I.C.E. and SmarterChild gained popularity for instant messaging. Then came voice assistants like Siri, Amazon Alexa, and Google Assistant, taking chatbots to new heights with voice interaction. These assistants exemplify chatbots utilizing voice assistance technology, bridging the gap between humans and AI.
Now, let's dive into the two main types of chatbots: Rule-based and Self-learning Chatbots.
Rule-based chatbots operate based on predefined rules and are limited in their outcomes. While they are simple and easy to implement, they struggle with ambiguous queries.
For instance, if a user asks about store hours, a rule-based chatbot can provide the predetermined answer. However, when faced with complex or undefined scenarios, these chatbots might fail to understand the context and provide relevant responses.

Empowering AI: Self-Learning Chatbots and the Journey Ahead
Self-learning chatbots employ machine-learning techniques to improve their performance over time. They learn from user interactions and inputs, adapting and generating responses based on patterns. Self-learning chatbots offer more flexibility and can handle a wider range of queries, providing personalized answers.
For example, when asked about finding a restaurant in a specific area, a self-learning chatbot can recommend a restaurant based on past interactions and preferences, which a rule-based chatbot might struggle with. However, self-learning chatbots require substantial initial training data and continuous updates to maintain accuracy and adapt to evolving technologies. Data privacy and security also pose challenges for self-learning chatbots, requiring developers to ensure proper measures are in place.

The Language Revolution: Using Natural Language Processing in Chatbots to Connect Users with Meaningful Conversations
NLP, as a part of AI, focuses on enabling computers to interact with humans using human languages. It plays a vital role in building chatbots by helping them understand and interpret data. There are various techniques involved in NLP, including Text Processing, Tokenization, Part-of-Speech tagging, Named Entity Recognition (NER), and Sentiment Analysis.
Text Processing is all about getting the text data ready for analysis. It involves cleaning and formatting the text, removing unnecessary characters, and stopping words that don't contribute much to the meaning. It's like tidying up the text for better understanding.
Tokenization, on the other hand, is the process of breaking down the text into individual words or tokens. It's like splitting a sentence into its building blocks.
Part-of-Speech Tagging (POS Tagging) is an important task in NLP. It involves assigning tags like nouns, adjectives, and verbs to the words in a text. By doing this, we can understand the grammatical structure and meaning of the sentences provided by users. It helps us make sense of how the words relate to each other.
Now, let's talk about Named Entity Recognition (NER). It's a powerful tool in today's world as it helps us identify and categorize named entities such as names, locations, and organizations. For instance, if a user tells a chatbot, "I would like to go to this restaurant at this place," NER can extract the specific location information mentioned. It's like having a chatbot that understands the context of the conversation.
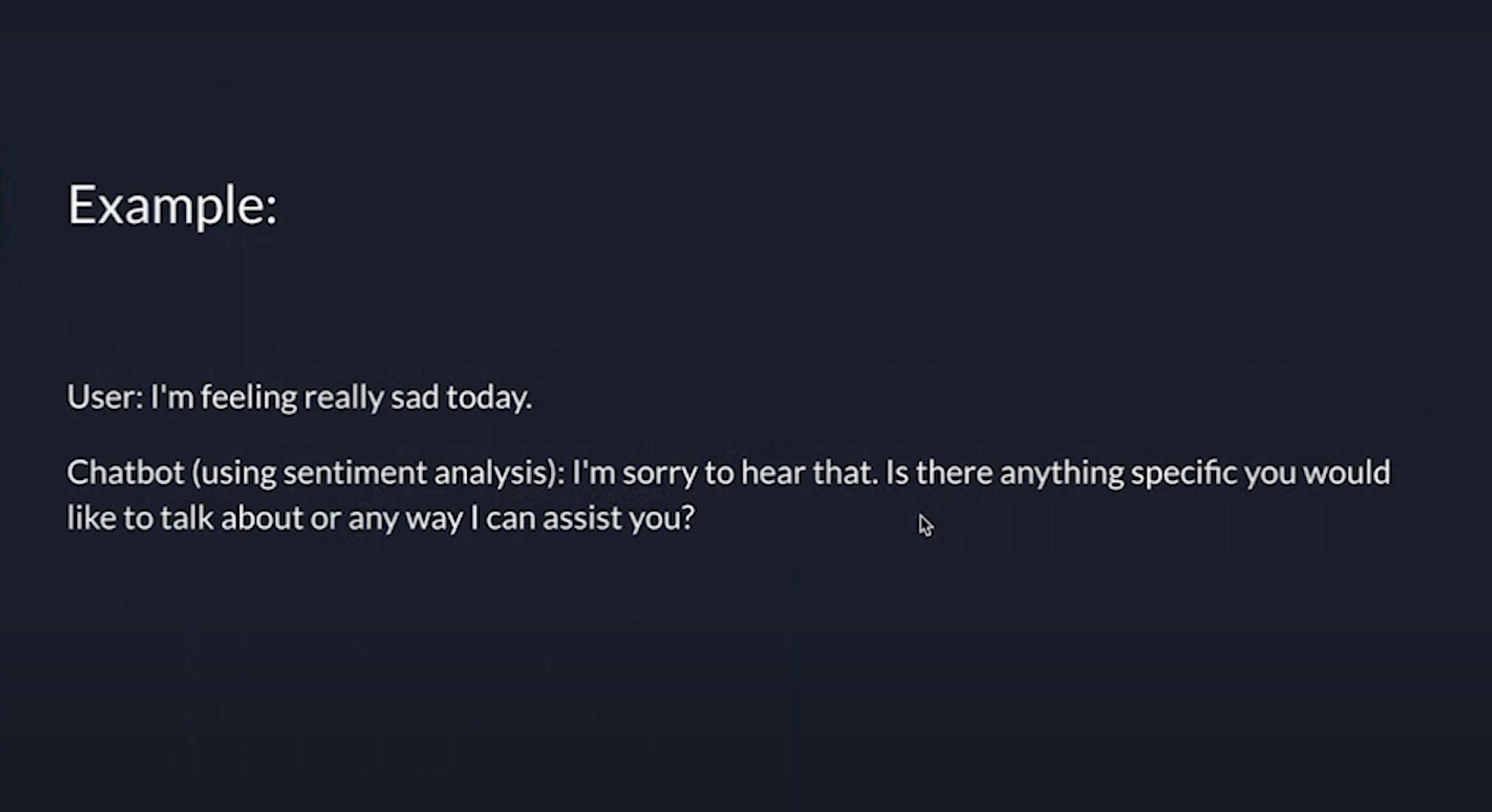
Lastly, Sentiment Analysis is a valuable part of NLP. It involves analyzing the sentiment or emotion expressed in the provided text. We can determine whether the text carries a positive, neutral, or negative sentiment. It helps chatbots gauge the user's emotions and respond accordingly. For example, if someone says, "I'm feeling really sad today," the chatbot can offer empathy and support.
“NLP opens up a world of possibilities for chatbots to understand and communicate with users in a more natural and meaningful way. It's like giving chatbots the power of language comprehension.”
Here's a simple example: if someone says, "I'm feeling really sad today," the chatbot can respond with, "I'm sorry to hear that." The chatbot understands the negative sentiment based on the sentiment analysis it has learned. It might then ask, "Is there anything specific you would like to talk about that I can assist you with?" This is how sentiment analysis works.
GPT-4 and OpenAI, the Technology Behind the Most Advanced Chatbots
Chatbots have immensely evolved with the help of transformer-based models like GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer). These models, developed by OpenAI, are at the forefront of language models and have revolutionized the chatbot landscape. What's impressive is that they use unsupervised learning, which means they don't rely on annotated datasets. Instead, they learn from a vast amount of books, articles, texts, and websites found on the internet. GPT-4, for instance, is trained on an extensive dataset without the need for human annotations. And if you're concerned about data security, it can even be hosted privately.
These transformer-based models employ powerful neural networks that enable them to understand patterns in text. They excel at predicting the next word in a sentence, leveraging their training on huge datasets to provide accurate responses. Just imagine asking a question like, "What are the best hiking trails in the area?" and the model generates answers based on its training. It's like having a knowledgeable companion who can provide helpful information.

Industries Leveraging the Power of Chatbots
E-commerce websites, for example, have integrated chatbots into their customer interactions. These chatbots can offer personalized recommendations based on a customer's previous purchases. For instance, if you buy a product on Amazon, the chatbot might suggest other products that customers bought alongside it. Additionally, chatbots have found extensive use in customer service, where human resources are only sometimes readily available. Customer service departments have improved efficiency and enhanced user experience by automating tasks, even simple ones.
The healthcare industry is another sector that heavily relies on AI and chatbots for customer interaction. Patients can describe their symptoms or problems, and chatbots can recommend the appropriate specialist they should contact. Human resources departments also make use of chatbots to assist employees with queries about rules and articles. We've even experimented with a "What Human Resources" chatbot for that purpose.
Not only these, but the travel industry and many other sectors have also embraced chatbots for various applications. The potential for chatbots to streamline processes, provide personalized assistance, and enhance customer experiences is vast.
Challenges and Limitations with the Current State of AI and Chatbots
Context understanding is an area of concern, especially when dealing with longer sentences. Rule-based chatbots can only handle limited context, and even larger language models like transformers still need help understanding ambiguous sentences or poorly written text. Another issue is the lack of real-time learning and memory, where chatbots struggle to maintain a coherent conversation and recall previous lines. In customer service, chatbots must understand the user's context and possess a long-term memory. Furthermore, the potential misuse of personal data raises privacy and security concerns. Proper measures must be taken to address these issues.
Looking towards the future, ongoing research in chatbot technology promises to make them even easier to use and understand, with multilingual capabilities. Continuous advancements in AI, driven by large language models, will contribute to this progress.
As for societal impacts and ethical considerations, addressing the potential job displacement caused by chatbot automation is essential. Transparent data privacy and security measures are vital to ensure user trust and mitigate the risk of misuse. Users should be informed when interacting with a chatbot and understand how their data will be used.
In conclusion, chatbots have become an integral part of various industries, and the advancements in large language models have greatly enhanced their capabilities. While challenges remain, such as context understanding and data privacy, chatbots can potentially revolutionize how we interact with technology. Continuous research and development will pave the way for more context-aware and efficient chatbots, reducing current limitations and enhancing user experiences.
To watch the full All Things AI Meetup, head over to GeekyAnts' YouTube channel.
Related Articles
Dive deep into our research and insights. In our articles and blogs, we explore topics on design, how it relates to development, and impact of various trends to businesses.