Table of Contents
Kickstarting Mobile Automation with Appium
Author

Date

Book a call
From Setup to Your First Test on Emulator and Real Device
- What Appium is and how it works
- Setting up your automation environment
- Running your first test on the emulator and real devices
- Common issues and how to fix them
What is Appium?
Appium is an open-source automation tool that allows you to test native, hybrid, and mobile web apps on both Android and iOS platforms — using the same API. Built on the WebDriver protocol (just like Selenium), Appium provides the flexibility to write tests in your favorite programming language.
Why Appium?
- No need to recompile or modify the app under test
- Supports Java, Python, JavaScript, Ruby, and more
- Works across Android and iOS platforms
- Completely free and actively maintained
Understanding Appium Architecture
Appium operates on a client-server model built over the WebDriver protocol. It acts as a bridge between your automation scripts and the mobile device — whether it’s an emulator, simulator, or a real phone. This architecture allows platform-independent test execution using a single API.
1. Appium Client
2. Appium Server
3. Automation Engines
- UIAutomator2 / Espresso (Android) – Executes commands on Android devices
- XCUITest (iOS) – Executes commands on an iOS device
4. Mobile Device (Emulator, Simulator, or Real Device)
5. Platform-Specific Bootstrap Components
How Appium Executes a Test Command
Here’s the complete flow of a single test command inside Appium’s architecture:
- Command Sent: Your test script (client) sends a command using WebDriver over HTTP (e.g., “Tap the Login button”).
- Server Processes: The Appium Server receives and parses the command, checks the desired capabilities to identify the platform.
- Routing to Engine: Based on the platform (Android/iOS), the server forwards the command to the correct automation engine.
- Interaction with Device: The engine acts as the app via the connected device or emulator.
- Response Returned: The result (success/failure) travels back through the engine and server to the test script.
Prerequisites Before You Begin
To get started with Appium, ensure the following software and tools are ready:
Required Tools:
- Java JDK (11 or higher)
- Node.js & npm
- Android Studio (for SDKs, emulator, platform tools)
- Appium CLI
- Appium Inspector
- Code Editor or IDE (e.g., IntelliJ, VS Code)
Programming Language Setup
Setting Up Your Automation Environment
Here’s a step-by-step installation guide:
1. Install Node.js & NPM
2. Install Appium CLI Globally
To start the server:
3. Verify Setup with Appium Doctor
It will check for missing dependencies, such as Java and Android tools.
4. Install Appium Inspector
5. Set Environment Variables
Then:
Android Studio & Emulator Setup
1. Install Android Studio
- Download from: https://developer.android.com/studio
2. Set Up SDK Tools
- Open Android Studio → SDK Manager
- Install: SDK Tools, Platform Tools, and Build Tools
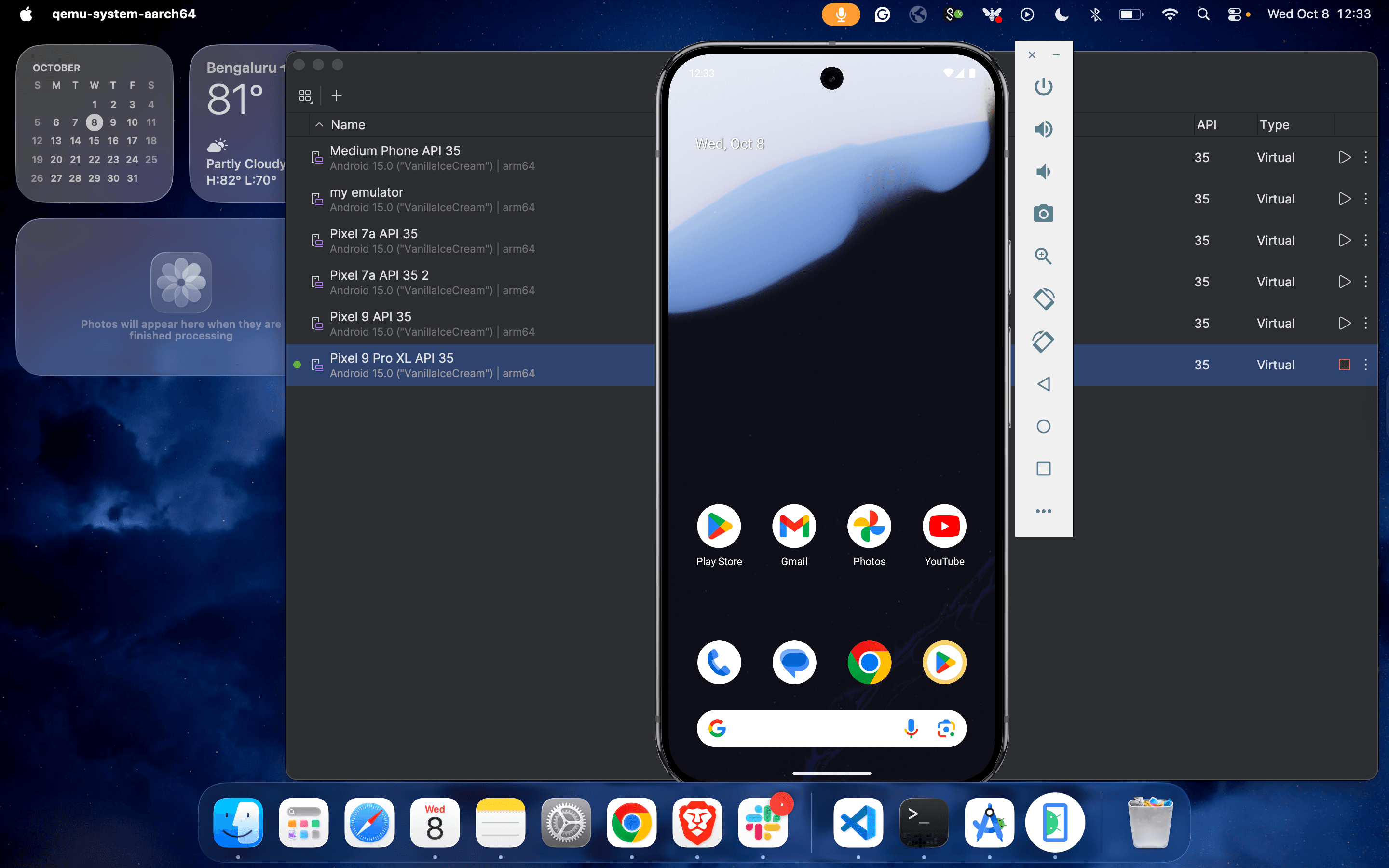
3. Create and Launch an Emulator
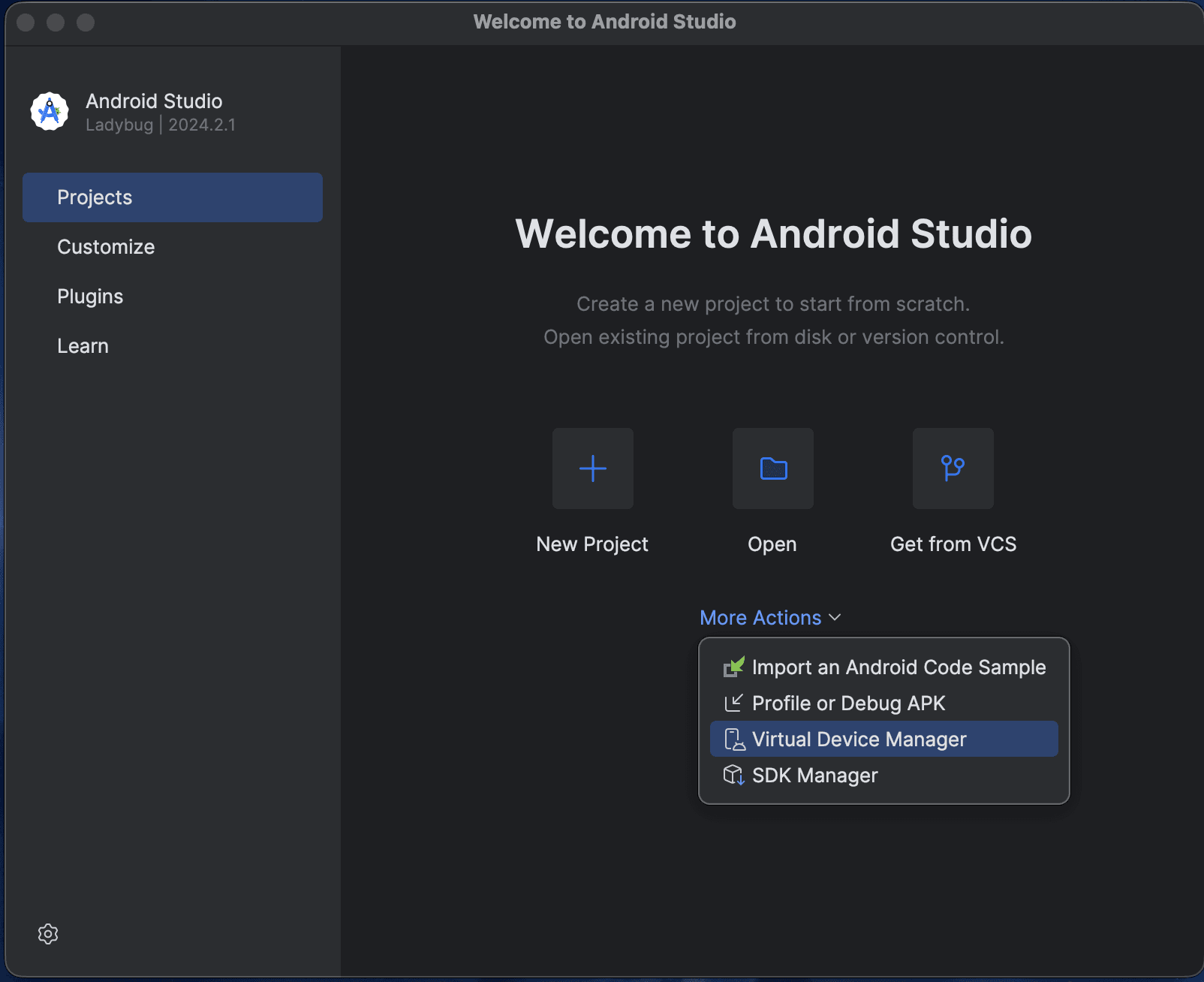
2. Under Device Manager, click on the plus icon to create a new virtual machine.
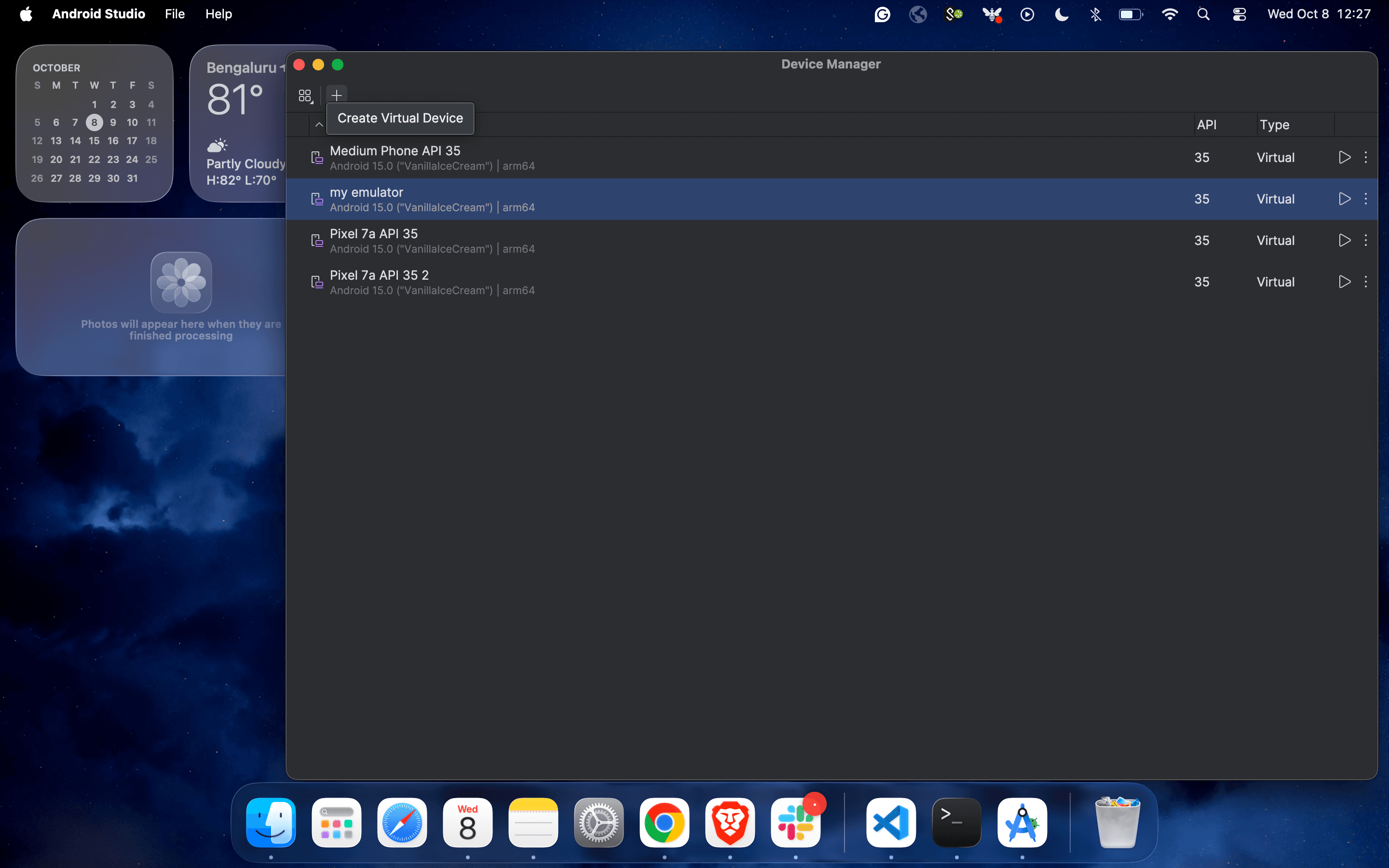
3. Select the device configuration from the list of virtual devices and click on “Next”.
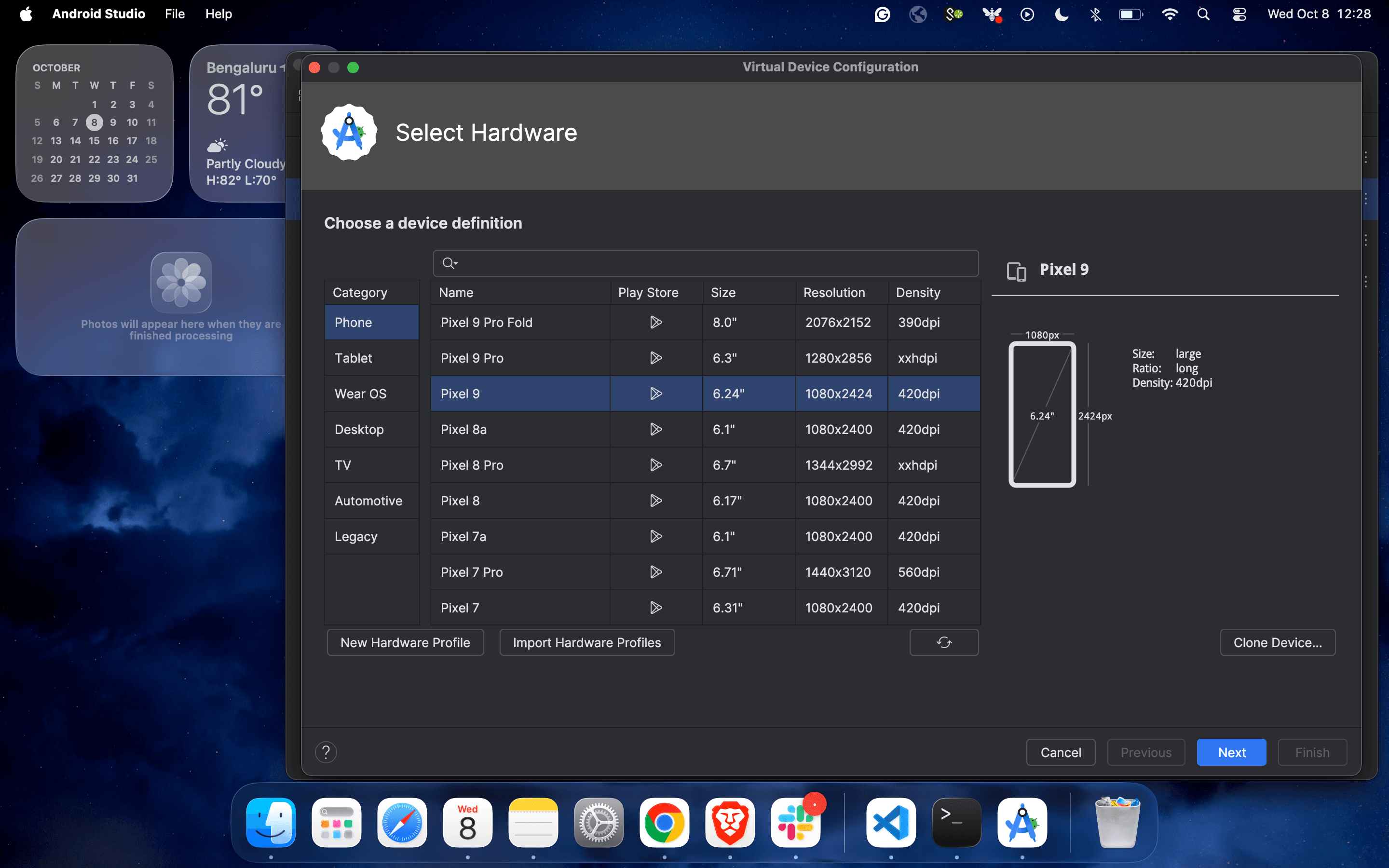
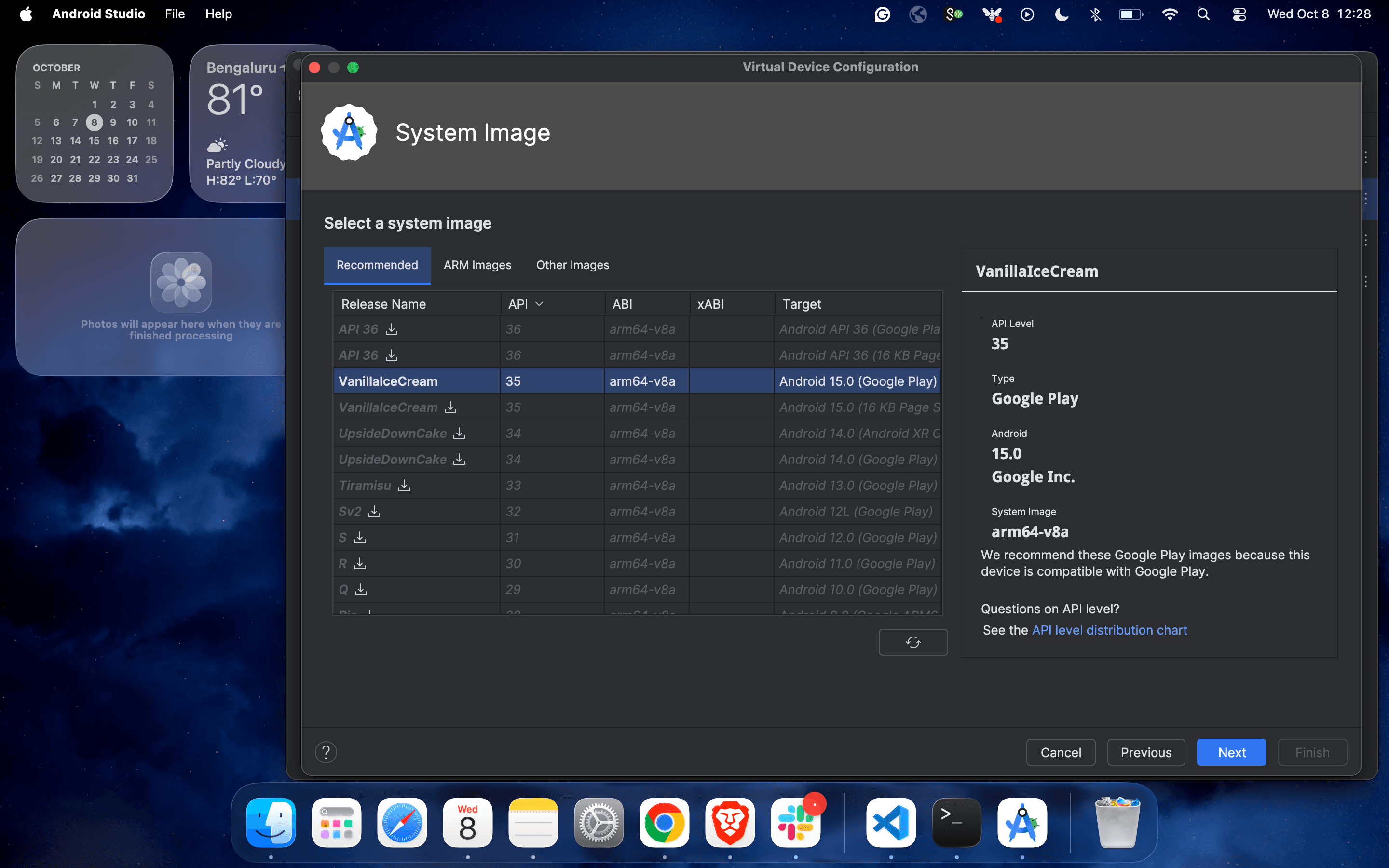
4. Complete the configuration process by selecting the operating Android version.
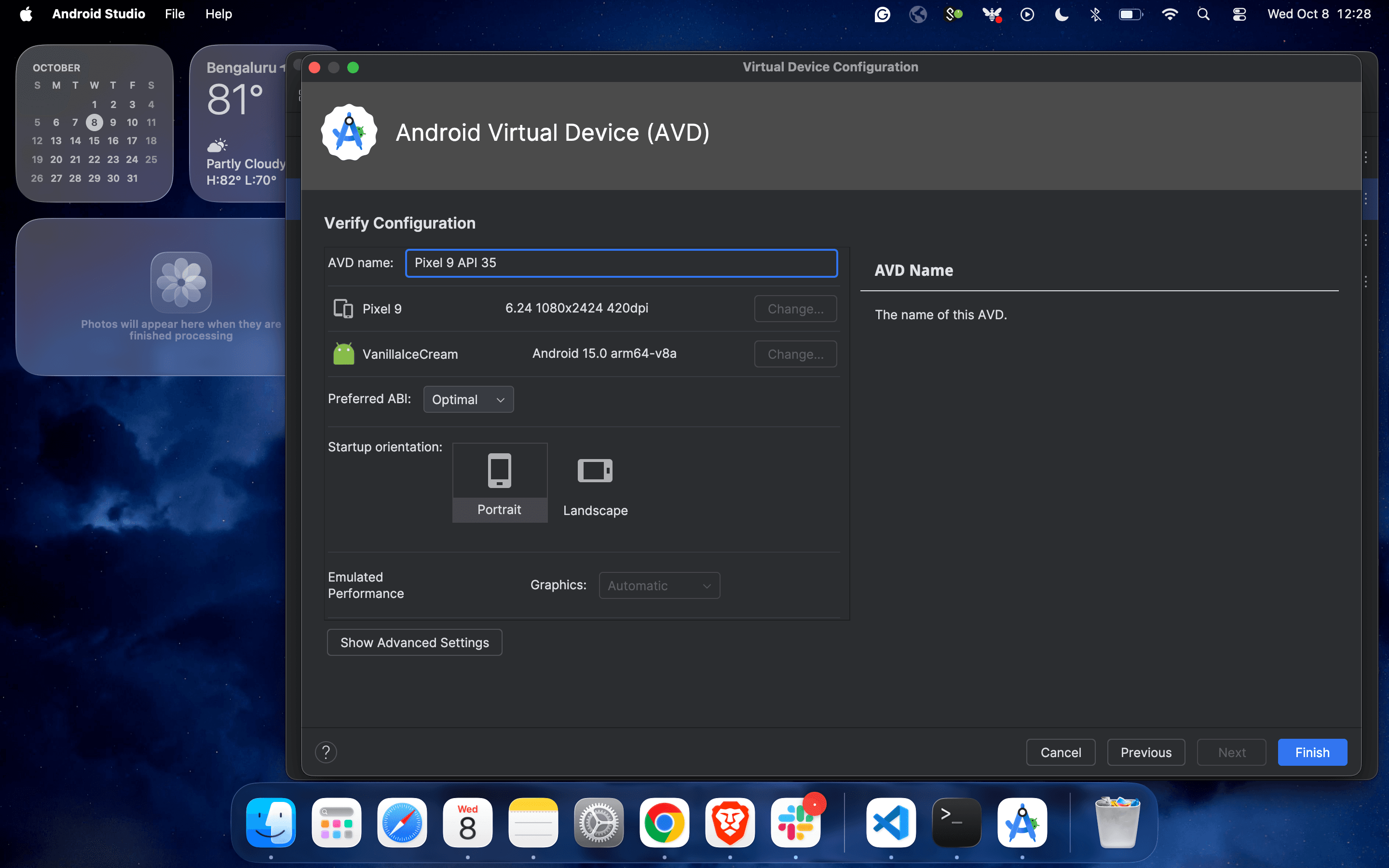
5. Update the name of the virtual device and click on “Finish”.
6. And you are almost done:
Getting Started with ADB (Android Debug Bridge)
ADB is a powerful command-line tool that lets you communicate with Android devices.
Common ADB Commands:
Make sure your device or emulator is listed:
Command to find App Package and App Activity:
Make sure the app is in a running state in the emulator/physical device.
Writing Your First Appium Test on Emulator
1. Define Desired Capabilities (JAVA):
Desired Capabilities for Appium Inspector to Inspect Mobile Elements:
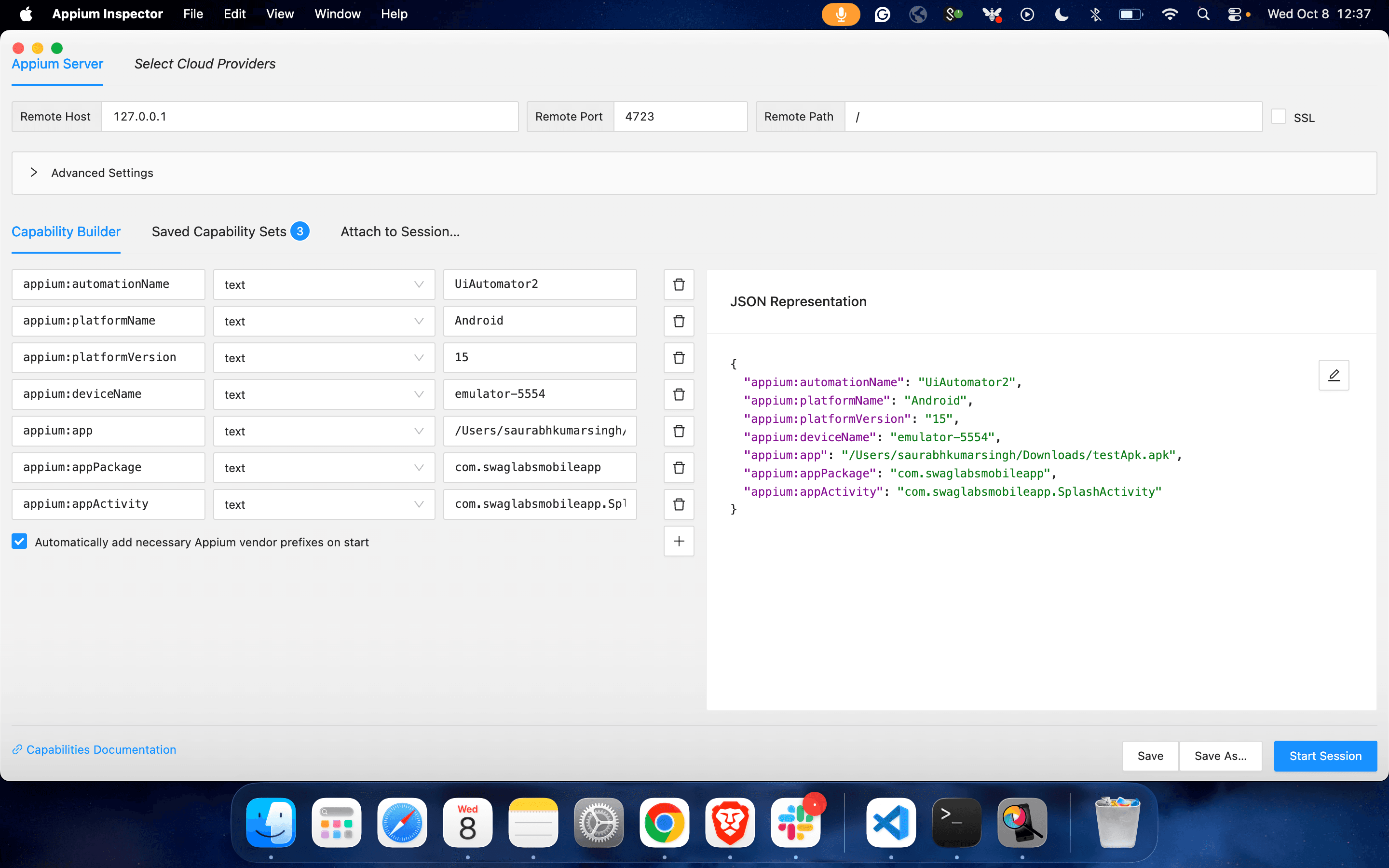
2. Sample Test Code: Launching Emulator Chrome Browser
Run the script using Maven(Archetype - Quickstart) or your IDE(IntelliJ IDEA).
3. POM.XML File
Running the Same Test on a Real Device
1. Prepare Your Device:
- Enable Developer Options and USB Debugging
- Connect via USB and authorize debugging.
- The above code needs Appium version 2.19.0
2. Update Desired Capabilities:
Your test should now run on the physical device.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
| Issue | Fix |
|---|---|
| Emulator not detected | Restart the emulator, check the adb devices |
| Appium server error | Restart the server, validate capabilities, and check the Java Client compatibility. |
| APK not installing | Check the path, permissions, or compatibility |
| Environment variable errors | Verify ANDROID_HOME, JAVA_HOME, and add to PATH |
Conclusion & What’s Next
Congratulations! You have just automated your first mobile test with Appium on both an emulator and a real device. In this journey, you’ve set up the environment, learned about ADB, and interacted with elements programmatically.