Table of Contents
Credit Card Fraud Detection and Prevention Strategies for Businesses in the USA
Author

Subject Matter Expert


Date

Book a call
Key Takeaways:
- Fraud prevention works best when built into digital card systems, not added as after-the-fact detection.
- Compliance frameworks and intelligent design together create the foundation of trust in the U.S. payments market.
- Institutions that embed resilience through secure architecture and adaptive intelligence turn fraud management into a competitive strength.
What Is Digital Credit Card Design?

Kunal Kumar
COO, GeekyAnts
Types of Credit Card Fraud & Their Impact
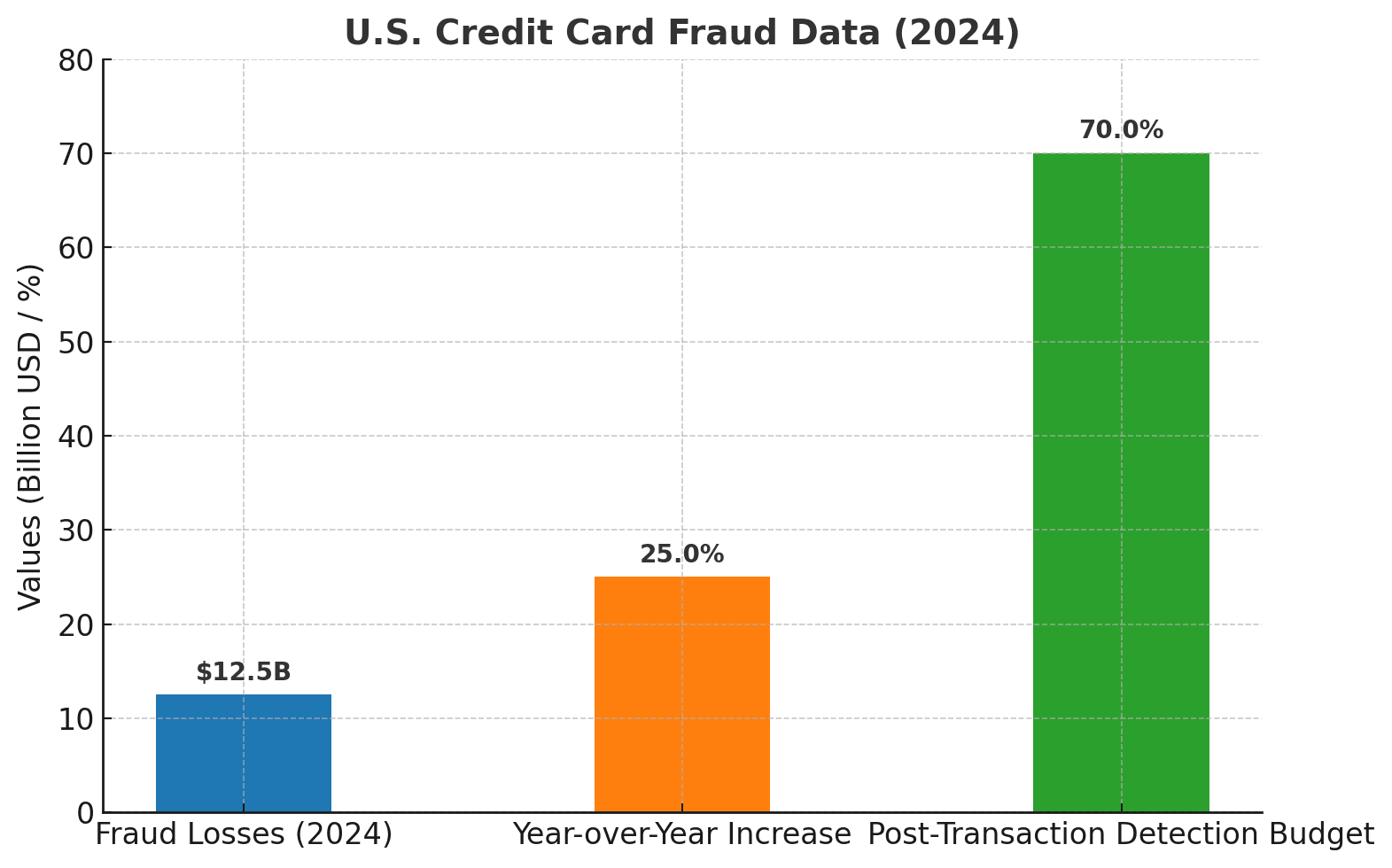
Credit card fraud occurs when stolen or compromised credentials are used to authorize transactions without the cardholder’s consent. In the United States, it has become the fastest-growing financial crime, fueled by the rise of digital payments and the sophistication of organized fraud networks. Losses go beyond financial impact: fraud undermines consumer confidence and erodes trust in the payments system.
Card-Not-Present (CNP) Fraud
Lost or Stolen Credentials
Account Takeovers
The Impact
How Can Credit Card Fraud Be Prevented and Detected?

Robin
GeekyAnts
To prevent fraud it should be equipped with systems that predict risk throughout the credit card lifecycle. Based on the experience of GeekyAnts with financial institutions, we pay attention to secure architecture, smart user controls, sophisticated analytics, and compliance-first design. The practices below are examples of how the practice of fraud prevention is changing nowadays.
Secure Payment Processing
EMV Chip Card Technology
Data and Database Design for Fraud Detection
Multifactor Authentication (MFA)
Machine Learning and Anomaly Detection
AVS and CVV Checks
Advanced Detection and Response Strategies
Fraud Detection Tools and Market Solutions (2023–2025)
Model and Operational Risk Management
Credit Card Lifecycle Risk Mitigation
Continuous Monitoring, Alerts, and Feedback Loops
U.S. Risk Frameworks & Regulatory Compliance
Compliance and fraud prevention cannot do without one another in the U.S. Data security, ongoing monitoring, and enterprise risk management frameworks are defined by such frameworks as the PCI DSS v4.0, NIST Cybersecurity and COSO governance. At the state level, rules such as CCPA and the NY DFS Cybersecurity Regulation widen these standards, introducing more rigid supervision and privacy demands. To financial institutions, compliance is worth more than mere fines- it has been proven to inspire trust in customers, mitigate systemic risk and make them resilient in the face of dynamic fraud strategies. In GeekyAnts, we build systems with compliance in architecture where fraud prevention and regulatory alignment are aligned as a strategic benefit.
Industries Most Exposed to Credit Card Fraud and a U.S. Banking Case Study on Real-Time Detection
Credit card fraud is not affecting every sector equally. Industries that have high transactions, where interactions are digital or low-margin are the most exposed. Online retail and e-commerce continue to be top targets because Card-Not-Present frauds take up digital commerce. Travel, gaming and hospitality platforms are the main targets of fraudsters due to the frequent cross-border transactions as well as the stored payment information. Services that are subscribed to are sensitive since the stolen credentials can be reused until it is detected. Legacy infrastructure and poor authentication frequently lead to ethe xploitation of fuel stations and other retail environments that have high POS. Last, although they can generate innovations, fintechs and neobanks are of a high-risk category where quick onboarding and online access open new attack paths. Fraud prevention is not optional in the case of these businesses since it is a core component of maintaining trust and competitiveness.
Case Study: Real-Time Fraud Detection in a U.S. Bank
How GeekyAnts Builds Resilient Credit Card Fraud Detection Systems

Kunal Kumar
COO, GeekyAnts
Credit card Fraud prevention demands precision in both design and execution. At GeekyAnts, we combine fintech expertise, regulatory alignment, and engineering depth to help institutions move from reactive monitoring to proactive fraud defense. Our work spans secure payment integrations, transaction monitoring platforms, and compliance-first mobile banking solutions, designed for banks, neobanks, and fintech startups operating in high-risk markets.
Why Institutions Choose GeekyAnts
- AI-Driven Detection → Adaptive machine learning models flag anomalies in real time across high-volume transactions.
- Compliance by Design → Architectures aligned with PCI DSS v4.0, GDPR, and SOC 2, ensuring regulatory trust from day one.
- Engineering Depth → Secure APIs, encrypted gateways, and cloud-native platforms that scale with evolving threats.
- Lifecycle Protection → Continuous monitoring across the card lifecycle—issuance, activation, usage, and closure.
- Proven Partnerships → Delivered white-labeled fintech platforms for financial institutions, strengthening resilience and accelerating time-to-market.
Conclusion
Fraud prevention is part of the system architecture, user experience, and compliance frameworks, and this is where resilience is realized. Secure design, dynamic intelligence and continuous monitoring make fraud management a cost of defence to a source of confidence and competitive power. Ambidexterity between these ideas in the card lifecycle will enable institutions to be in the best position to safeguard customers, their expectations by the regulations and keep up with the changing threats.
FAQs
1. How is the best prevention of credit card fraud done?
2. What are the effects of the PCI DSS compliance on the detection of fraud?
3. What is the best ML model to use with real-time fraud scoring?
4. Which behavior design brings behavioral changes to lessen misuse?
5. What is the best way of dealing with model risk in banks?
6. What are the advantages of fuel fraud?
Dive deep into our research and insights. In our articles and blogs, we explore topics on design, how it relates to development, and impact of various trends to businesses.