Table of Contents
How AI is Optimizing Patient Care and Clinical Trials
Author

Date

Book a call
In 2024, a patient at Moorfields Eye Hospital in London was swiftly diagnosed with diabetic retinopathy thanks to an AI system developed by DeepMind. What once required a specialist's availability and multiple appointments was now handled with precision and speed—transforming the patient journey entirely.
Stories like this are no longer outliers. Artificial intelligence (AI) is changing patient care and clinical research. It offers more accurate diagnoses, personalised treatments, and quicker drug development. Healthcare is now entering a time where data-driven intelligence is not helping with decisions. It's reshaping what we can achieve.
This blog explores how AI is improving outcomes at both ends of the healthcare continuum - patient-facing care and behind-the-scenes clinical innovation. With real-world case studies and strategic recommendations to back it up, we decode the technologies, trends, and ethical dimensions that are shaping this shift.
The Role of AI in Modern Healthcare
Artificial intelligence is becoming integral to healthcare, using machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and predictive analytics to interpret vast, complex medical data. These systems identify patterns, forecast outcomes, and support clinical decisions at a scale beyond human capability.
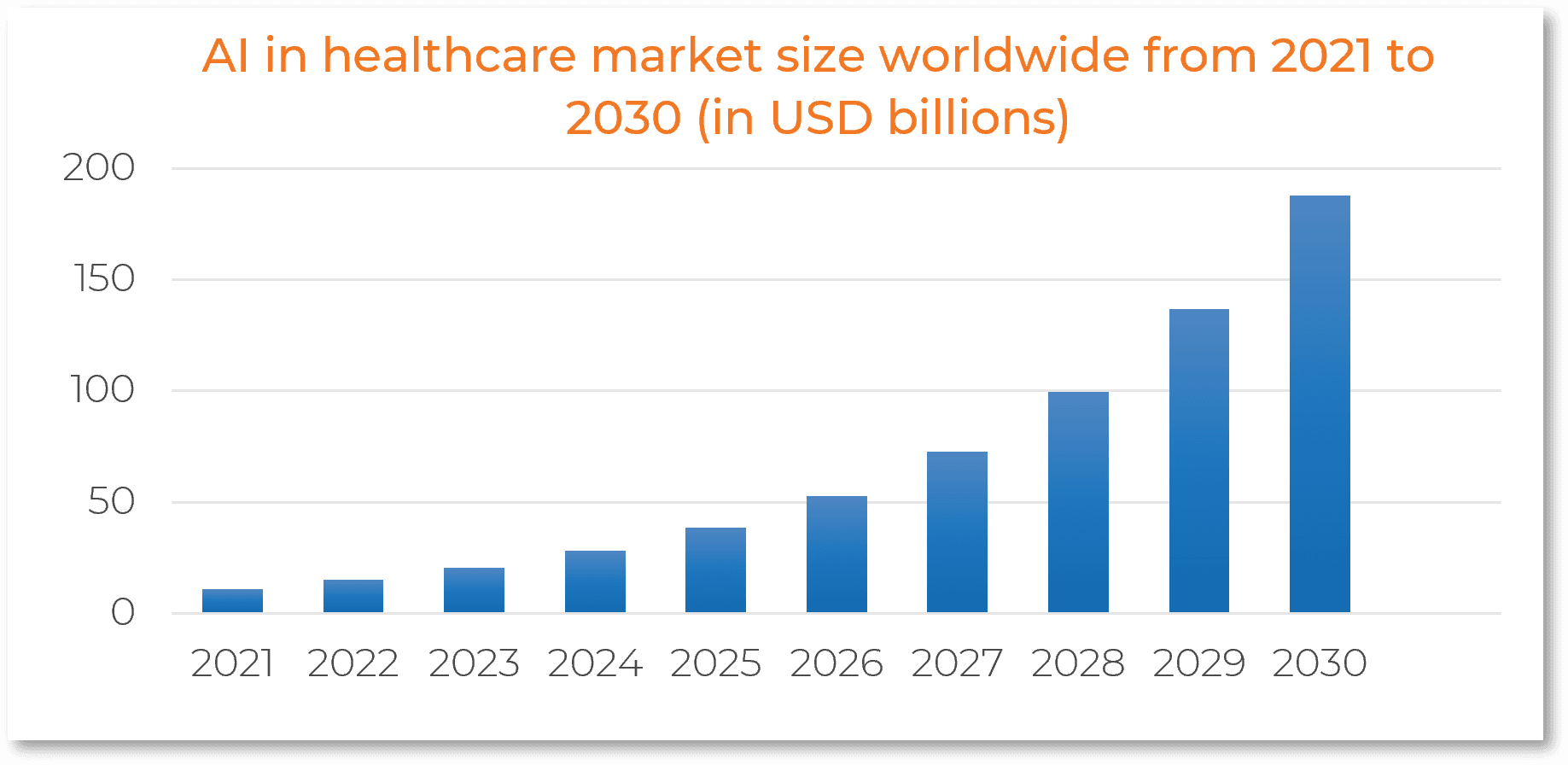
Driven by the need for precision and scalability, healthcare providers and pharmaceutical companies are embedding AI into diagnostics, treatment planning, and administrative workflows. According to Statista, the global AI healthcare market is projected to exceed $187 billion by 2030—underscoring its role as a core driver of modern, data-powered care delivery.
AI Enhancing Patient Care
Improving Diagnostic Accuracy
AI systems can detect subtle patterns in imaging, lab reports, and electronic health records (EHRs) to help doctors make faster and more accurate diagnoses. DeepMind’s AI model, for example, was trained on over 15,000 eye scans and achieved diagnostic accuracy on par with expert clinicians. Similarly, AI tools used in oncology can now identify cancers at earlier stages, improving survival rates through timely intervention.
Personalized Treatment Plans
By analyzing a patient’s genetic data, lifestyle factors, and medical history, AI platforms can tailor treatment strategies to the individual. Sanofi, for instance, uses AI to create targeted therapies for infectious diseases, resulting in better patient responses and fewer side effects.
Operational Efficiency
AI is also optimizing hospital operations. At Duke Health, GE Healthcare’s Command Center software analyzes real-time data to predict patient admission rates and optimize resource allocation. This not only reduces wait times but also improves the overall patient experience.
AI Transforming Clinical Trials
Accelerating Patient Recruitment
Identifying and enrolling suitable participants is one of the most time-consuming aspects of clinical trials. AI platforms can analyze EHRs, genomic databases, and social determinants of health to match patients with trials more efficiently. Companies have reported that recruitment timelines are shortened by over 30% using AI-driven tools.
Smarter Trial Design
AI helps design trials by simulating different trial scenarios and identifying potential bottlenecks. This leads to better-structured studies with fewer protocol amendments—an area where nearly 60% of trials currently face delays.
Real-Time Monitoring and Data Integrity
AI enables continuous monitoring of trial data, detecting anomalies or safety concerns as they arise. This not only ensures compliance but also allows adaptive trial designs where protocols can be adjusted on the fly based on participant responses.
Ethical and Regulatory Considerations
While the potential of AI is enormous, its integration into healthcare must be done responsibly.
- Data Privacy: AI systems require access to vast datasets, raising concerns about patient confidentiality. Regulatory frameworks like HIPAA in the U.S. and GDPR in Europe are evolving to address this.
- Algorithmic Bias: If trained on non-diverse datasets, AI models can produce biased outcomes. Ensuring representation across gender, race, and age groups is essential to ethical AI deployment.
- Regulatory Compliance: AI tools must meet stringent clinical validation standards. Regulatory bodies like the FDA are now creating specialized pathways for AI/ML-based medical software.
AI in Action: Impact and the Road Ahead
Healthcare systems are already realizing the benefits of AI. HCA Healthcare uses AI to detect sepsis risk early, resulting in a 30% improvement in timely diagnosis. At University Hospitals in Cleveland, AI reviews radiology reports in real time—accelerating intervention for strokes and hemorrhages.
Looking ahead, AI is poised to drive continuous care through wearable integration, virtual health assistants, and intelligent mental health platforms. To stay ahead, healthcare leaders must:
- Upskill clinical teams to work effectively with AI tools
- Forge strategic collaborations with AI startups and research labs
- Establish robust ethical and regulatory frameworks
These actions not only ensure responsible AI adoption but they position healthcare organizations to deliver faster, safer, and more personalized care at scale.
Conclusion
AI is redefining how healthcare systems operate—from diagnostic precision and personalized care to streamlined clinical trials and continuous patient monitoring. Its impact is measurable, but scaling it responsibly requires more than algorithms. It demands robust governance, cross-functional expertise, and strategic execution.
Healthcare organizations that embed AI thoughtfully will lead in outcomes, innovation, and efficiency.
GeekyAnts builds custom AI-powered healthcare solutions tailored for long-term impact.





